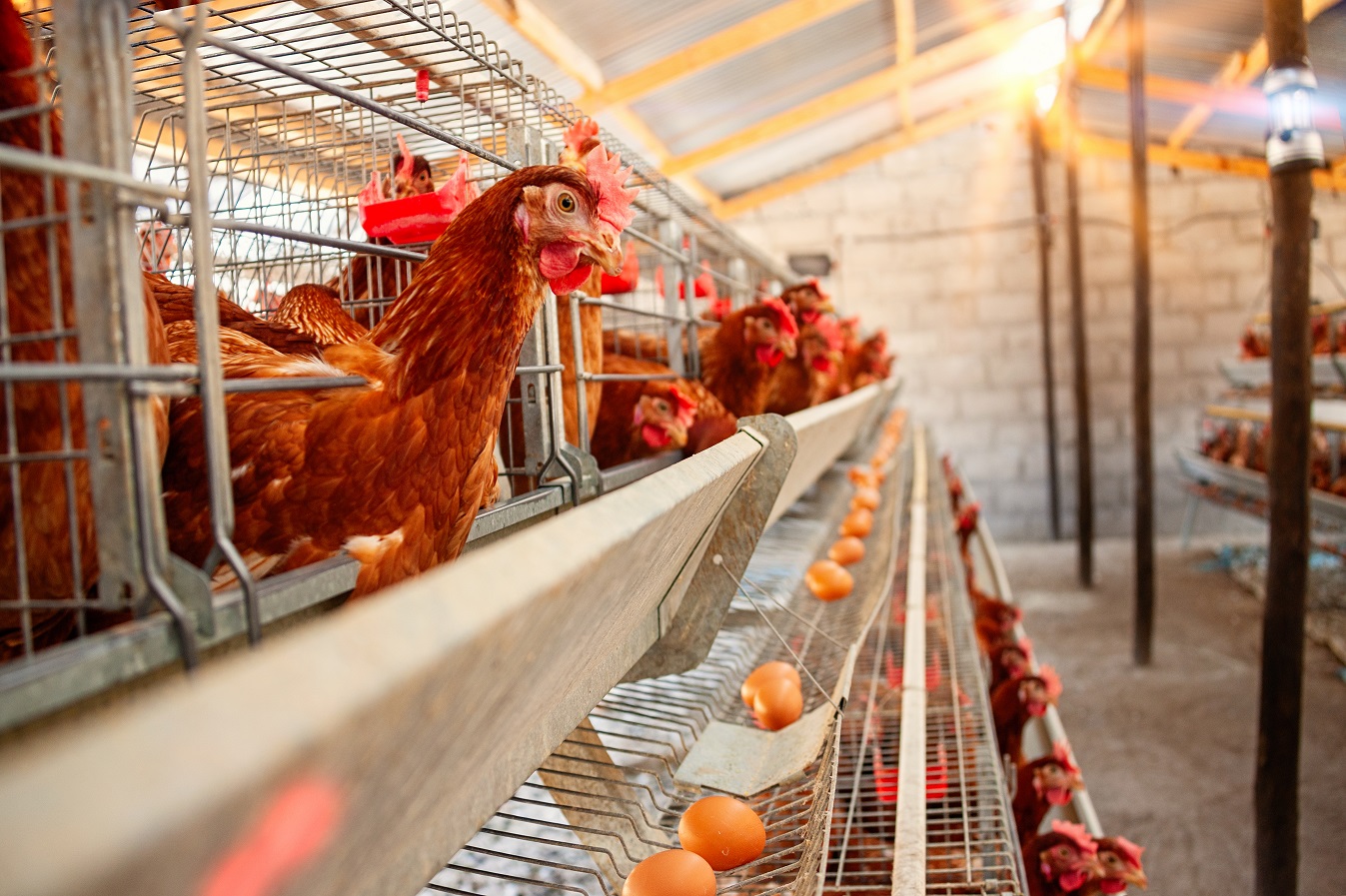
Disinfection in agriculture and farms
TERMECA as a water-based pesticide can destroy bacterial, fungal and viral agents through the destruction of the outer shell quickly and effectively. TERMECA can be used for high-level disinfection of agricultural soil, halls and equipment in greenhouses irrigation systems and water tanks in greenhouses, and seed disinfection
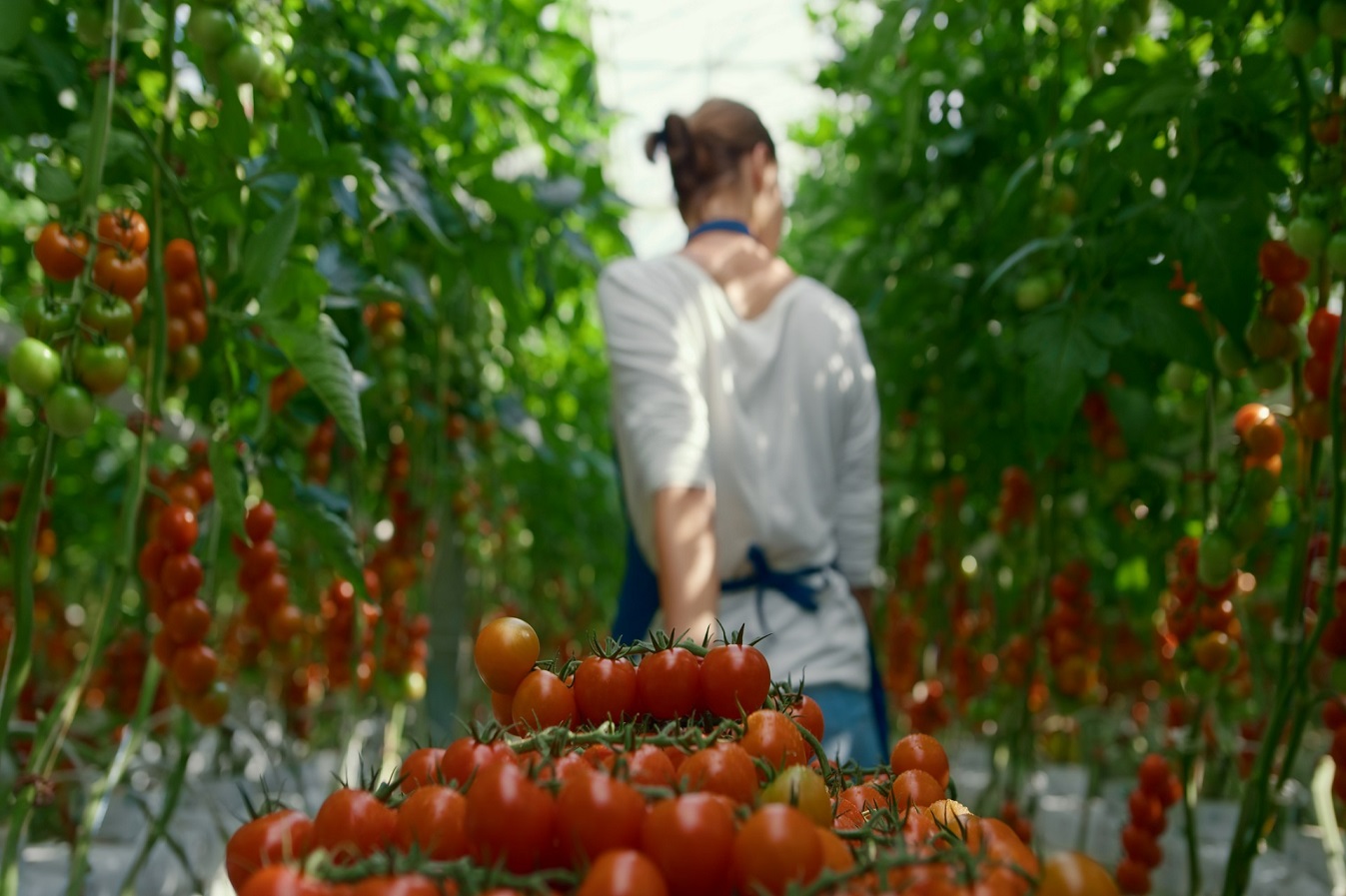

Chemical poisons, including pesticides, fungicides and herbicides, are substances that are used to prevent, destroy or repel pests, including harmful insects and molluscs, plant diseases and weeds. Most of the poisons that can be used in agriculture include organochlorine, phosphorus (organophosphorus) or carbamates. Although the use of pesticides is necessary for farmers, they pose many risks to human health and the environment.
Chemical poisons are very harmful not only to the health of users but also to the health of consumers of agricultural products. Because the first point of contact with poison in humans is the skin; As soon as the body is exposed to the poison, the poison is absorbed in the body or remains only in the skin without being absorbed and can cause eye irritation, respiratory problems, acute poisoning and skin allergies. Also, the probability of cancer in workers who are exposed to toxins is twice as high as in other people. For example, farmers who use alachlor poison in their work environment are 50% more prone to colon cancer than other people.
On the other hand, eating food products in which chemical poisons have penetrated can increase the number of toxic substances in the human body and cause symptoms of poisoning and illness such as headache, fever, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea, heart palpitations and sweating. The fact of chemical poisoning by poisons used in agricultural products is similar to the symptoms caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses and fungi.
According to the research carried out regarding sustainable agriculture, pesticides can cause miscarriage, lack of intellectual development of babies, interference in hormonal actions, sterility of men and women, as well as irregular menstrual periods in women.
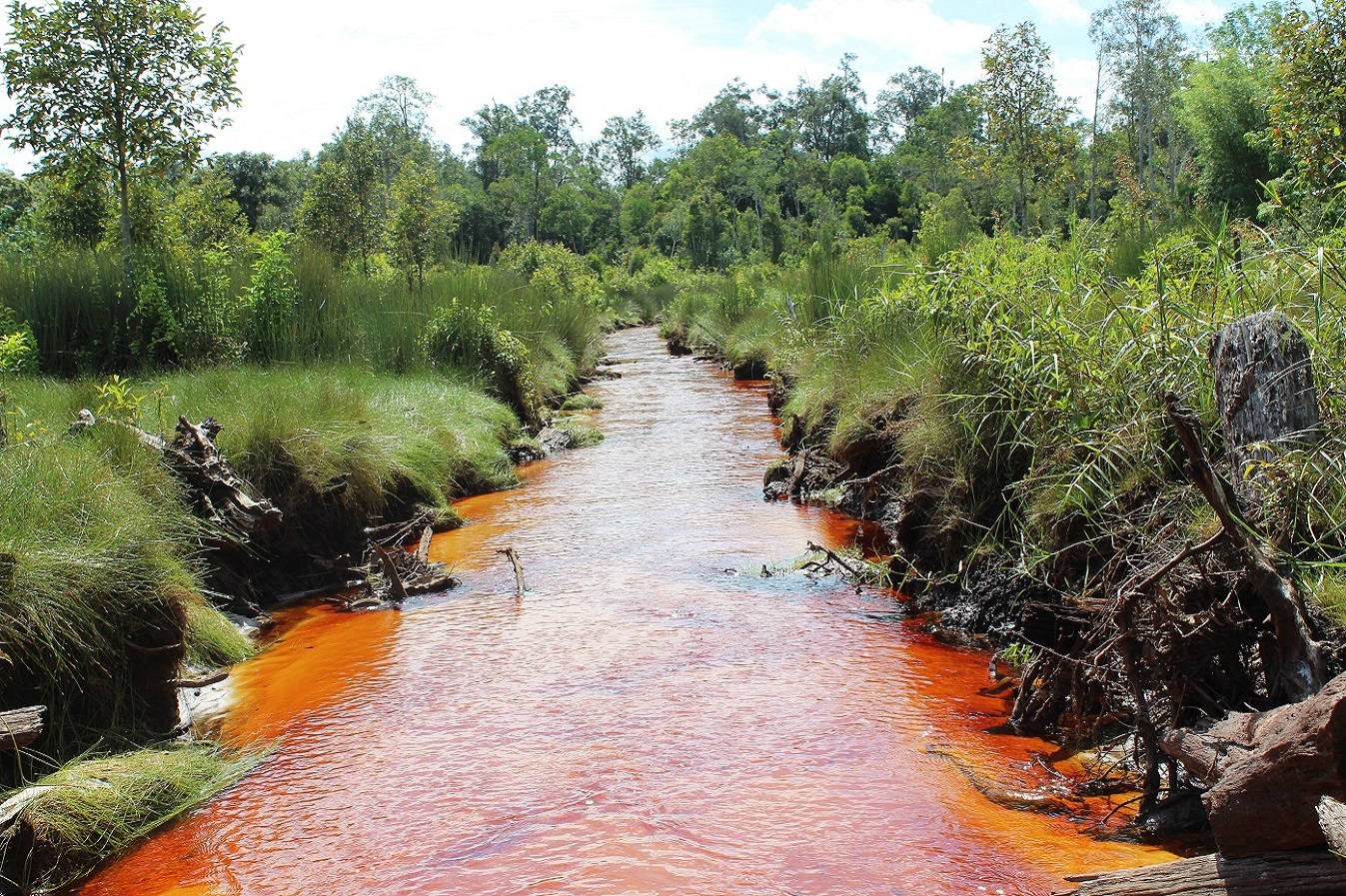
These toxins are also very harmful to the environment because on the one hand, nitrates caused by the consumption of toxins and chemical fertilisers cause pollution of wetlands, rivers and seas and lead to the death of aquatic animals and plants, on the other hand, these are released through evaporation or They enter the atmosphere directly through the air and pollute the soil along with the rain.
Therefore, it seems that to achieve sustainable agriculture and preserve human health and the environment, increase biodiversity, soil fertility and stability, should be provided as solutions to reduce the consumption of chemical poisons. In this regard, several methods have been proposed by researchers:
Organic farming: In this system, the use of chemical fertilizers, poisons and additives is limited or eliminated. This system is based on crop rotation and residues, animal manures, green manures, off-farm organic waste, mechanical cultivation, minerals, use of biological methods for soil productivity, nutrient supply, insect control, and weeds. Based. But this method also has disadvantages. this type of agriculture is time-consuming and organic products are very expensive, as a result, they do not have high consumer demand. Secondly, if organic agriculture is not well managed, it causes microbiological pollution. For example, manure (as a carrier of human pathogenic bacteria) becomes dangerous to human health as a form of organic fertilizer if not properly composted, and contamination of organic products may occur during packaging, processing and storage. Organic farming is not a simple process.
Biological farming: In this method, biological pesticides are used that are obtained from plants, animals, microorganisms or minerals (for example, canola oil or baking soda). They are non-toxic and more compatible with the environment. But these pesticides also have disadvantages, for example, they are sensitive to sunlight, they must be kept at a temperature between 4 and 10 degrees Celsius, and they have a short duration and must be used regularly. As a result, also due to storage and transportation limitations, biological pesticide is more expensive than chemical pesticide.
Microbial insecticides: Microbial insecticides destroy baby pests and do not involve the dangers of penetrating poisons, and even if they remain on the crops, they do not cause immediate reactions due to the small number of chemicals left in the crops. but in case of continuous and long-term use, the residues of insecticides affect the nervous system, respiratory system and digestive system.
Today's farmers are facing issues such as water resource management, climate change and global warming, and a diversity of pests and plant diseases that can destroy all their efforts in a short time. Therefore, they are looking for low-cost and simple methods to reduce the cost of the finished product and reduce the use of water and the frequency of spraying with pesticides. Incorrect use of pesticides can increase the frequency of spraying, use more poisons, reduce yield and lose the optimal time to fight against pests.
Water is the most important liquid that is used as a carrier of herbicides and insecticides in spraying.
Most common herbicides are water soluble and can be sprayed. Clarity and the presence of minerals in water affect the effectiveness of some herbicides, for example, water hardness, water pH, the number of bicarbonate ions, water turbidity and organic matter, iron and other substances present in it affect the absorption and transfer of some herbicides.
Some pesticides break down quickly when added to water with a very high ph. In this situation, even before the start of spraying, the lethal poison turns into an inert non-lethal substance. Therefore, the use of water-based pesticides such as TERMECA with a certain concentration can not only quickly and effectively destroy bacterial, fungal and viral agents through the destruction of the outer shell, but also the problems related to spraying It does not contain pesticide solutions.
Because after combining TERMECA with water, it turns into oxygen and water while maintaining its pesticidal ability and does not leave any harmful residue, so it does not harm the environment.
TERMECA can be used for high-level disinfection of agricultural soil, disinfection of halls and equipment in greenhouses, disinfection of irrigation systems and water tanks in greenhouses, and seed disinfection. It can also be a suitable substitute for fungicides in agricultural fields and greenhouses and it can even be used to remove algae from the water source.
Chemical poisons are very harmful not only to the health of users but also to the health of consumers of agricultural products. Because the first point of contact with poison in humans is the skin; As soon as the body is exposed to the poison, the poison is absorbed in the body or remains only in the skin without being absorbed and can cause eye irritation, respiratory problems, acute poisoning and skin allergies. Also, the probability of cancer in workers who are exposed to toxins is twice as high as in other people. For example, farmers who use alachlor poison in their work environment are 50% more prone to colon cancer than other people.
On the other hand, eating food products in which chemical poisons have penetrated can increase the number of toxic substances in the human body and cause symptoms of poisoning and illness such as headache, fever, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea, heart palpitations and sweating. The fact of chemical poisoning by poisons used in agricultural products is similar to the symptoms caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses and fungi.
According to the research carried out regarding sustainable agriculture, pesticides can cause miscarriage, lack of intellectual development of babies, interference in hormonal actions, sterility of men and women, as well as irregular menstrual periods in women.
These toxins are also very harmful to the environment because on the one hand, nitrates caused by the consumption of toxins and chemical fertilisers cause pollution of wetlands, rivers and seas and lead to the death of aquatic animals and plants, on the other hand, these are released through evaporation or They enter the atmosphere directly through the air and pollute the soil along with the rain.
Therefore, it seems that to achieve sustainable agriculture and preserve human health and the environment, increase biodiversity, soil fertility and stability, should be provided as solutions to reduce the consumption of chemical poisons. In this regard, several methods have been proposed by researchers:
Organic farming: In this system, the use of chemical fertilizers, poisons and additives is limited or eliminated. This system is based on crop rotation and residues, animal manures, green manures, off-farm organic waste, mechanical cultivation, minerals, use of biological methods for soil productivity, nutrient supply, insect control, and weeds. Based. But this method also has disadvantages. this type of agriculture is time-consuming and organic products are very expensive, as a result, they do not have high consumer demand. Secondly, if organic agriculture is not well managed, it causes microbiological pollution. For example, manure (as a carrier of human pathogenic bacteria) becomes dangerous to human health as a form of organic fertilizer if not properly composted, and contamination of organic products may occur during packaging, processing and storage. Organic farming is not a simple process.
Biological farming: In this method, biological pesticides are used that are obtained from plants, animals, microorganisms or minerals (for example, canola oil or baking soda). They are non-toxic and more compatible with the environment. But these pesticides also have disadvantages, for example, they are sensitive to sunlight, they must be kept at a temperature between 4 and 10 degrees Celsius, and they have a short duration and must be used regularly. As a result, also due to storage and transportation limitations, biological pesticide is more expensive than chemical pesticide.
Microbial insecticides: Microbial insecticides destroy baby pests and do not involve the dangers of penetrating poisons, and even if they remain on the crops, they do not cause immediate reactions due to the small number of chemicals left in the crops. but in case of continuous and long-term use, the residues of insecticides affect the nervous system, respiratory system and digestive system.
Today's farmers are facing issues such as water resource management, climate change and global warming, and a diversity of pests and plant diseases that can destroy all their efforts in a short time. Therefore, they are looking for low-cost and simple methods to reduce the cost of the finished product and reduce the use of water and the frequency of spraying with pesticides. Incorrect use of pesticides can increase the frequency of spraying, use more poisons, reduce yield and lose the optimal time to fight against pests.
Water is the most important liquid that is used as a carrier of herbicides and insecticides in spraying.
Most common herbicides are water soluble and can be sprayed. Clarity and the presence of minerals in water affect the effectiveness of some herbicides, for example, water hardness, water pH, the number of bicarbonate ions, water turbidity and organic matter, iron and other substances present in it affect the absorption and transfer of some herbicides.
Some pesticides break down quickly when added to water with a very high ph. In this situation, even before the start of spraying, the lethal poison turns into an inert non-lethal substance. Therefore, the use of water-based pesticides such as TERMECA with a certain concentration can not only quickly and effectively destroy bacterial, fungal and viral agents through the destruction of the outer shell, but also the problems related to spraying It does not contain pesticide solutions.
Because after combining TERMECA with water, it turns into oxygen and water while maintaining its pesticidal ability and does not leave any harmful residue, so it does not harm the environment.
TERMECA can be used for high-level disinfection of agricultural soil, disinfection of halls and equipment in greenhouses, disinfection of irrigation systems and water tanks in greenhouses, and seed disinfection. It can also be a suitable substitute for fungicides in agricultural fields and greenhouses and it can even be used to remove algae from the water source.
.jpg)



















_1.jpg)